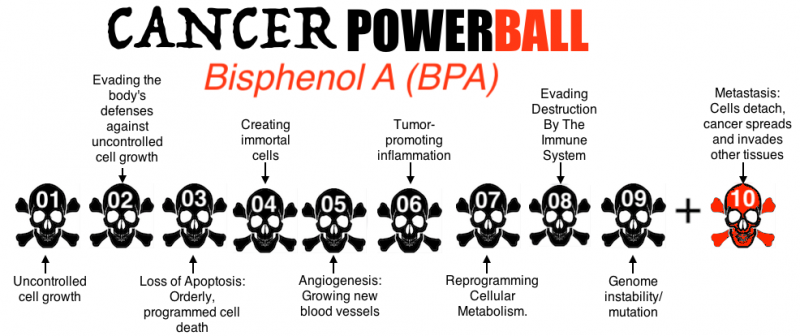
Bisphenol A can give you an instant “win” because it can check off all 10 Cancer Powerball numbers PLUS it hinders the effectiveness of cancer treatment drugs/chemotherapy.
This article is one of a new series to help intelligent non-scientists understand the confusing probabilities of how chemicals, genetics, radiation and other factors can cause cancer.
It’s vital to understand that just because BPA (Bisphenol A) can trigger 10 factors present at the same time doesn’t mean a cancer will inevitably develop.
However it does mean that BPA primes all the conditions necessary for a cancer to occur.
This ad-free article is made possible by the financial support of the
Center for Research on Environmental Chemicals in Humans: a 501(c)(3) non-profit.
Please consider making a tax-deductible donation for continued biomedical research.
Read this — and the other articles below — for a deeper understanding.
NOTE: Recent and representative examples of published, peer-reviewed scientific papers showing how BPA triggers the various Hallmarks are linked below, and categorized by which of the Hallmarks of Cancer they trigger. Because there are so many studies, we have selected a representative sample, usually from 2015 or newer.
Many papers also examine more than one Hallmark and appear more than once.
In addition, the search turned up links that involve anti-cancer therapies designed to target one or more Hallmarks of Cancer, thus offering further scientific credibility of addressing Hallmarks as indicators of carcinogenesis.
Those anti-therapeutic characteristics of BPA are topics that the Stealth Syndromes project has addressed previously:
- Precision evaluation of environmental chemical risk assessment: Using existing pharmaceutical evaluation results as a more accurate paradigm
- Strongest Evidence Yet Between BPA and Thyroid Cancer
- Heat Shock Protein Hsp27 points to causal link between BPA and cancer & chemotherapy resistance
01 – Bisphenol uncontrolled cell growth proliferation
- Disruptive environmental chemicals and cellular mechanisms that confer resistance to cell death (Study indicates that BPA activates 9 Hallmarks: 01, 02, 03, 04, 05, 06, 07, 09, 10)
- Submicromolar [very low does] bisphenol A (BPA) concentrations induced proliferation and DNA damage
- “BPA exerts its effects through deregulating cell signaling pathways associated with cell growth, proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis“
- A mini review of bisphenol A (BPA) effects on cancer-related cellular signaling pathways
- Bisphenol -A-induced inactivation of the p53 axis underlying deregulation of proliferation kinetics, and cell death in non-malignant human breast epithelial cells
- Bisphenol-A impairs cellular function and alters DNA methylation of stress pathway genes in first trimester trophoblast cells
- Bisphenol A induces proliferative effects on both breast cancer cells and vascular endothelial cells through a shared GPER-dependent pathway in hypoxia
- Low doses of bisphenol A stimulate the proliferation of breast cancer cells via ERK1/2/ERRγ signals
- The molecular mechanisms of action of the endocrine disrupting chemical bisphenol A in the development of cancer
02 – Bisphenol evading cell growth control
- Mechanisms of environmental chemicals that enable the cancer hallmark of evasion of growth suppression
- Assessing the carcinogenic potential of low-dose exposures to chemical mixtures in the environment: the challenge ahead
- Disruptive environmental chemicals and cellular mechanisms that confer resistance to cell death
- The potential for chemical mixtures from the environment to enable the cancer hallmark of sustained proliferative signalling
Bisphenol A (BPA) and cell signaling pathways
03 – Bisphenol apoptosis cell death
- A mini review of bisphenol A (BPA) effects on cancer-related cellular signaling pathways
- Bisphenol A (BPA) and cell signaling pathways
- Disruptive environmental chemicals and cellular mechanisms that confer resistance to cell death
- Capsaicin, a Spicy Component of Hot Pepper, Induces Apoptosis by Activation of the Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor γ in HT-29 Human Colon Cancer Cells
- A mini review of bisphenol A (BPA) effects on cancer-related cellular signaling pathways
- Xenoestrogen interference with nongenomic signaling actions of physiological estrogens in endocrine cancer cells
- The potential for chemical mixtures from the environment to enable the cancer hallmark of sustained proliferative signalling
04- Bisphenol cell immortality
- Disruptive chemicals, senescence and immortality
05 – Bisphenol angiogenesis
- Phthalate metabolites and bisphenol-A in association with circulating angiogenic biomarkers across pregnancy
- Bisphenol-A impairs cellular function and alters DNA methylation of stress pathway genes in first trimester trophoblast cells
- The potential for chemical mixtures from the environment to enable the cancer hallmark of sustained proliferative signalling
- BISPHENOL A ENHANCES GROWTH OF Hep-G2 CANCER CELLS BY UPREGULATING EXPRESSION OF PRO – INFLAMMATORY AND PRO – ANGIOGENESIS PROTEINS
- Bisphenol A promotes X‐linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein‐dependent angiogenesis via G protein‐coupled estrogen receptor pathway
- Bisphenol A induces proliferative effects on both breast cancer cells and vascular endothelial cells through a shared GPER-dependent pathway in hypoxia
- Assessing the carcinogenic potential of low-dose exposures to chemical mixtures in the environment: focus on the cancer hallmark of tumor angiogenesis
- Bisphenol A triggers proliferation and migration of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma via GPER mediated upregulation of IL‐6
06 – Bisphenol inflammation
- Environmental immune disruptors, inflammation and cancer risk
- Bisphenol-A Impairs Insulin Action and Up-Regulates Inflammatory Pathways in Human Subcutaneous Adipocytes and 3T3-L1 Cells
- Bisphenol A (BPA) the mighty and the mutagenic
- BISPHENOL A ENHANCES GROWTH OF Hep-G2 CANCER CELLS BY UPREGULATING EXPRESSION OF PRO – INFLAMMATORY AND PRO – ANGIOGENESIS PROTEINS
- The molecular mechanisms of action of the endocrine disrupting chemical bisphenol A in the development of cancer[oxidative stress]
- Oxidative stress and cancer: an overview.
- Bisphenol A triggers proliferation and migration of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma via GPER mediated upregulation of IL‐6
- Oxidative stress, inflammation, and cancer: How are they linked?
- Chronic inflammation and oxidative stress as a major cause of age-related diseases and cancer.
- Hypoxia, oxidative stress and inflammation
07 – Bisphenol cancer cellular metabolism
- Targeting energy metabolism to eliminate cancer cells
- Assessing the carcinogenic potential of low-dose exposures to chemical mixtures in the environment: the challenge ahead
- The potential for chemical mixtures from the environment to enable the cancer hallmark of sustained proliferative signalling
08 – Bisphenol immune evasion
- Chemical compounds from anthropogenic environment and immune evasion mechanisms: potential interactions
- Bisphenol A: A notorious player in the mosaic of autoimmunity
- Assessing the carcinogenic potential of low-dose exposures to chemical mixtures in the environment: the challenge ahead
09 – Bisphenol genetic instability
- Bisphenol A impairs the double-strand break repair machinery in the germline and causes chromosome abnormalities
- Causes of genome instability: the effect of low dose chemical exposures in modern society
- Bisphenol A impairs the double-strand break repair machinery in the germline and causes chromosome abnormalities.
- Bisphenol A (BPA) the mighty and the mutagenic
- The potential for chemical mixtures from the environment to enable the cancer hallmark of sustained proliferative signalling
- Assessing the carcinogenic potential of low-dose exposures to chemical mixtures in the environment: the challenge ahead
- The Genotoxic and Cytotoxic Effects of Bisphenol-A (BPA) in MCF-7 Cell Line and Amniocytes
10 – Bisphenol migration invasion, metastasis
- Bisphenol A (BPA) and cell signaling pathways
- Assessing the carcinogenic potential of low-dose exposures to chemical mixtures in the environment: the challenge ahead
- A mini review of bisphenol A (BPA) effects on cancer-related cellular signaling pathways
- A mini review of bisphenol A (BPA) effects on cancer-related cellular signaling pathways
- The impact of low-dose carcinogens and environmental disruptors on tissue invasion and metastasis
- Bisphenol A triggers proliferation and migration of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma via GPER mediated upregulation of IL‐6
10A – A subcategory about epithelial mesenchymal/transition (cell transformation)
- Epithelial – mesenchymal transition: A special focus on phthalates and bisphenol a
- Bisphenol A modulates colorectal cancer protein profile and promotes the metastasis via induction of epithelial to mesenchymal transitions
- Bisphenol A stimulates the epithelial mesenchymal transition of estrogen negative breast cancer cells via FOXA1 signals
- Effects of bisphenol compounds on the growth and epithelial mesenchymal transition of MCF-7 CV human breast cancer cells
- Bisphenol A-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition is mediated by cyclooxygenase-2 up-regulation in human endometrial carcinoma cells
- Low dose of bisphenol A modulates ovarian cancer gene expression profile and promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition via canonical Wnt pathway
- A mini review of bisphenol A (BPA) effects on cancer-related cellular signaling pathways
- … epithelial mesenchymal transition related with cancer progression and metastasis and potential effects of endocrine disrupting chemicals on epithelial mesenchymal …
- Bisphenol S (BPS) triggers the migration of human non-small cell lung cancer cells via upregulation of TGF-β
- Bisphenol A and nonylphenol have the potential to stimulate the migration of ovarian cancer cells by inducing epithelial – mesenchymal transition via an estrogen …
Examples of table excerpts (Right click on tables, below, to view larger images)
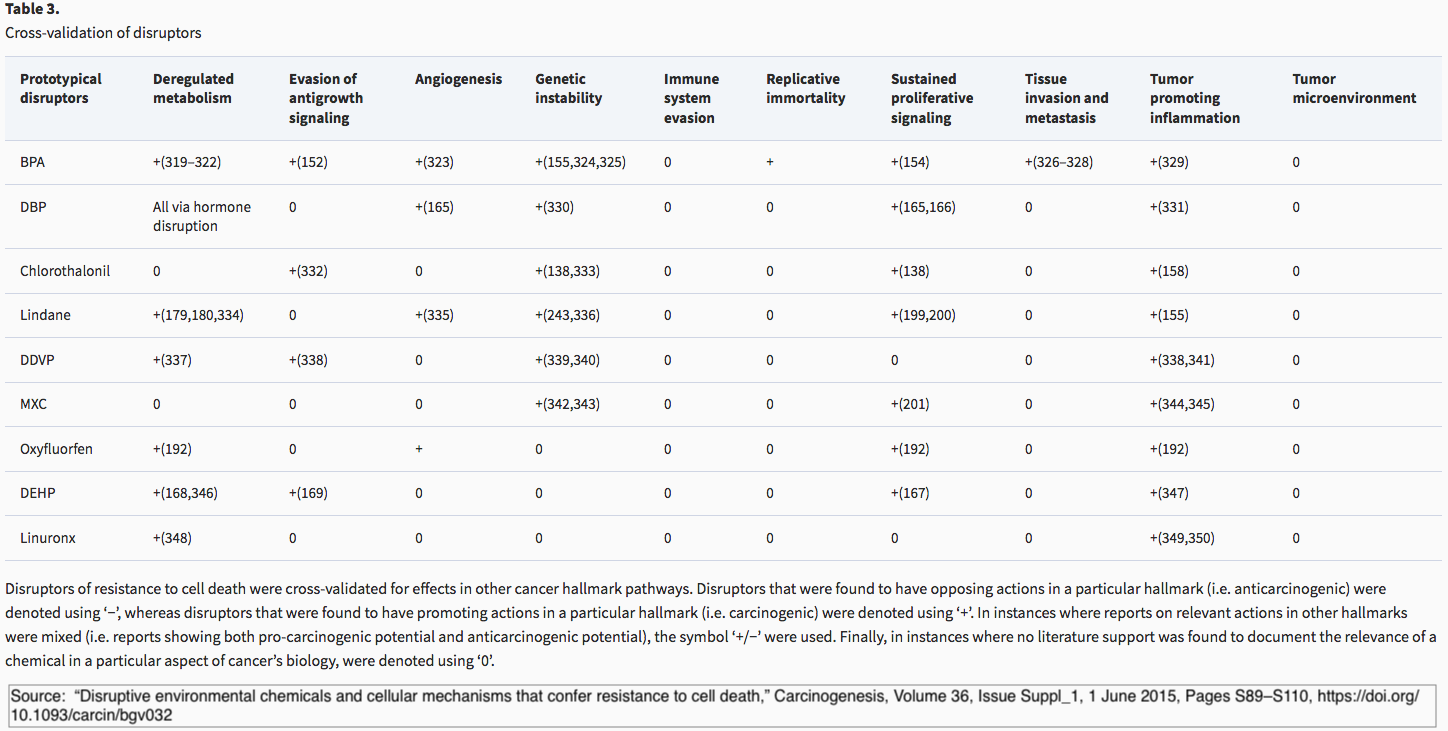
From: Disruptive environmental chemicals and cellular mechanisms that confer resistance to cell death
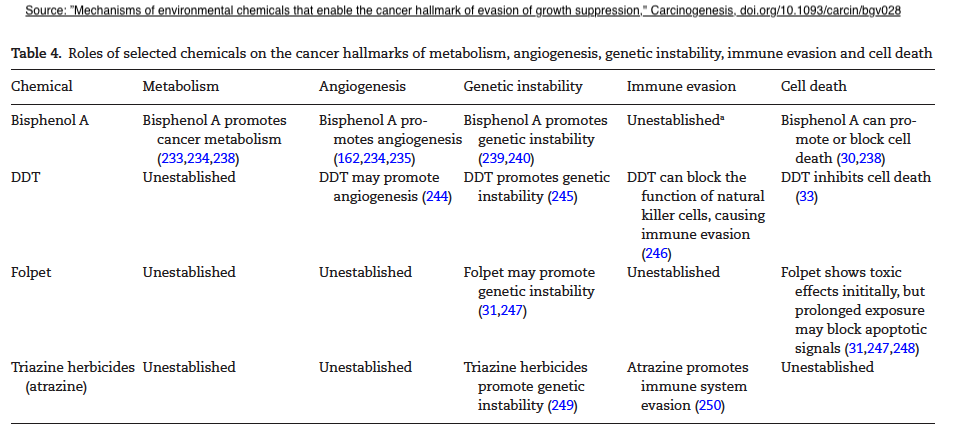
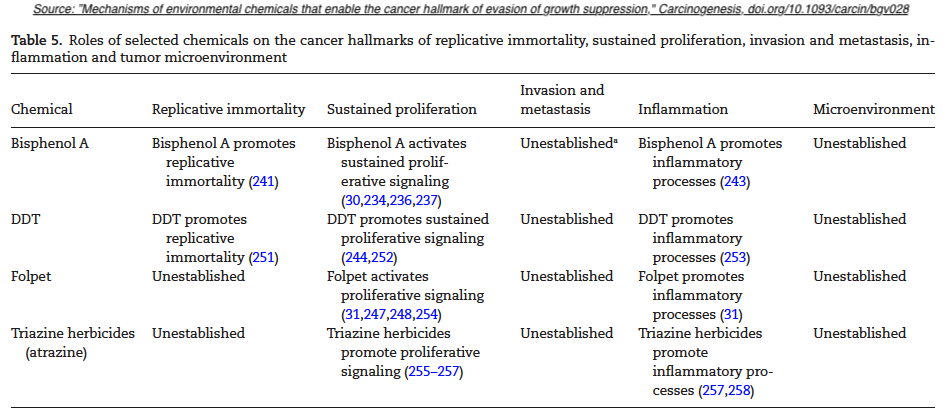
From: Disruptive environmental chemicals and cellular mechanisms that confer resistance to cell death
Pharmaceutical confirmation: Looking for a cure by addressing specific Cancer Powerball numbers (Hallmarks)
- Regulation of cell signaling pathways by dietary agents for cancer prevention and treatment
- Naringenin inhibits proliferation, migration, and invasion as well as induces apoptosis of gastric cancer SGC7901 cell line by downregulation of AKT pathway
- Chemo resistance A mini review of bisphenol A (BPA) effects on cancer-related cellular signaling pathways
- Chemo resistanceBisphenol A at the reference level counteracts doxorubicin transcriptional effects on cancer related genes in HT29 cells.
Additional Sources:
- Bisphenol A (BPA) and cell signaling pathways [metabolic disorder, obesity][brain, nervous system]
- Chronic exposure to bisphenol a impairs progesterone receptor-mediated signaling in the uterus during early pregnancy[infertility]
- Endocrine disruptors and the tumor microenvironment: A new paradigm in breast cancer biology
- The molecular mechanisms of action of the endocrine disrupting chemical bisphenol A in the development of cancer[epigenetics, behavior ..more]
- Molecular mechanisms of the preventable causes of cancer in the United States
- A Ternary Mixture of Common Chemicals Perturbs Benign Human Breast Epithelial Cells More Than the Same Chemicals Do Individually
- Effects of bisphenol A on metabolism and evidences of a mode of action mediated through endocrine disruption
- Cytotoxicity of seven bisphenol analogues compared to bisphenol A and relationships with membrane affinity data
- Bisphenol A – Sources, toxicity and biotransformation [exposure sources]
- Evidence for bisphenol A-induced female infertility: a review (2007–2016)
- A systematic review on the role of environmental toxicants in stem cells aging
- Cytotoxic effects of composite dust on human bronchial epithelial cells
- BPA exposure is associated with non-monotonic alteration in ESR1 promoter methylation in peripheral blood of men and shorter relative telomere length in peripheral blood of women
- The regulation of cellular apoptosis by the ROS-triggered PERK/EIF2α/chop pathway plays a vital role in bisphenol A-induced male reproductive toxicity
- Bisphenol A – Sources, toxicity and biotransformation
A paper worth extra attention
Comments are closed.